Understanding gas, Gwei, and cost saving strategies
Have you ever wondered why at certain parts of the day, the price to deploy a smart contract, or to mint a token can be fairly affordable, and at other times astronomical in price?
In this article, we will cover the relationship between gas and Gwei, network priority, what causes these fluctuations, and best practices to know to maximize transacting efficiently.
Gas⛽
Gas is a unit of measurement used to express the computational work needed to perform specific operations on the Ethereum blockchain. Every transaction, such as sending Ether (ETH) or interacting with a smart contract, requires a certain amount of gas to be executed. The more complex the operation, the higher the amount of gas required. Gas ensures that the resources used by the network are fairly distributed among users and prevents spamming or abuse of the network.
Gwei 🪙
Gwei (short for gigawei) is a small denomination of Ether, the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum blockchain. 1 Ether is equal to 1,000,000,000 Gwei. Gwei is commonly used to set the gas price for transactions, which is the amount of Ether a user is willing to pay for each unit of gas consumed by a transaction.
Now, let's understand how gas and Gwei are related:
When you submit a transaction on the Ethereum network, you need to specify the gas price in Gwei. This is basically your "bid" for how much you're willing to pay for each unit of gas required to perform the transaction. Nodes, who validate and process transactions, are incentivized to prioritize transactions with higher gas prices since they earn more fees in return.
The total cost of a transaction is determined by multiplying the gas price (in Gwei) by the amount of gas required for the transaction. For example, if a transaction requires 100,000 gas and you set the gas price to 20 Gwei, the total transaction cost would be 2,000,000 Gwei or 0.002 Ether.
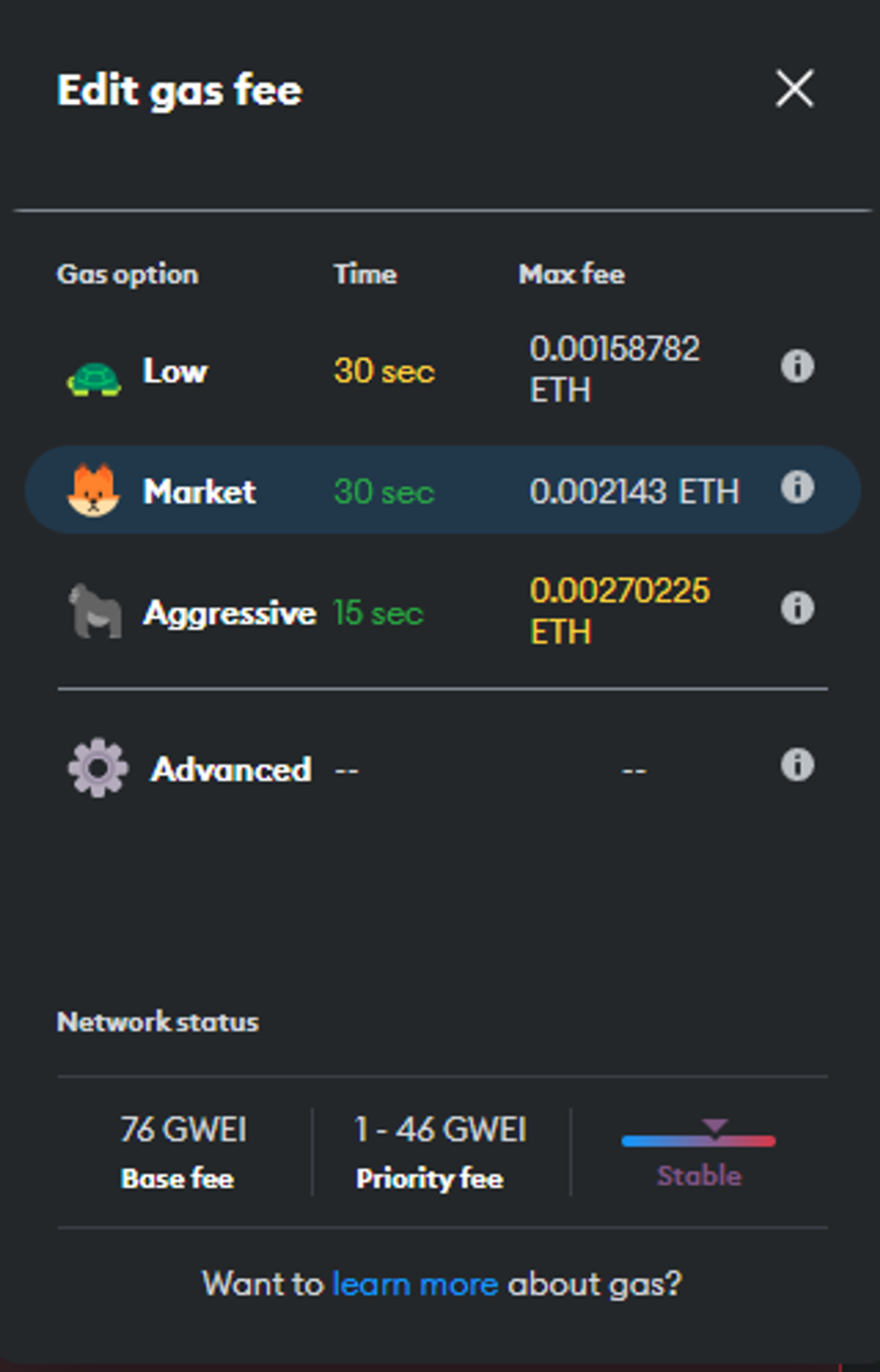
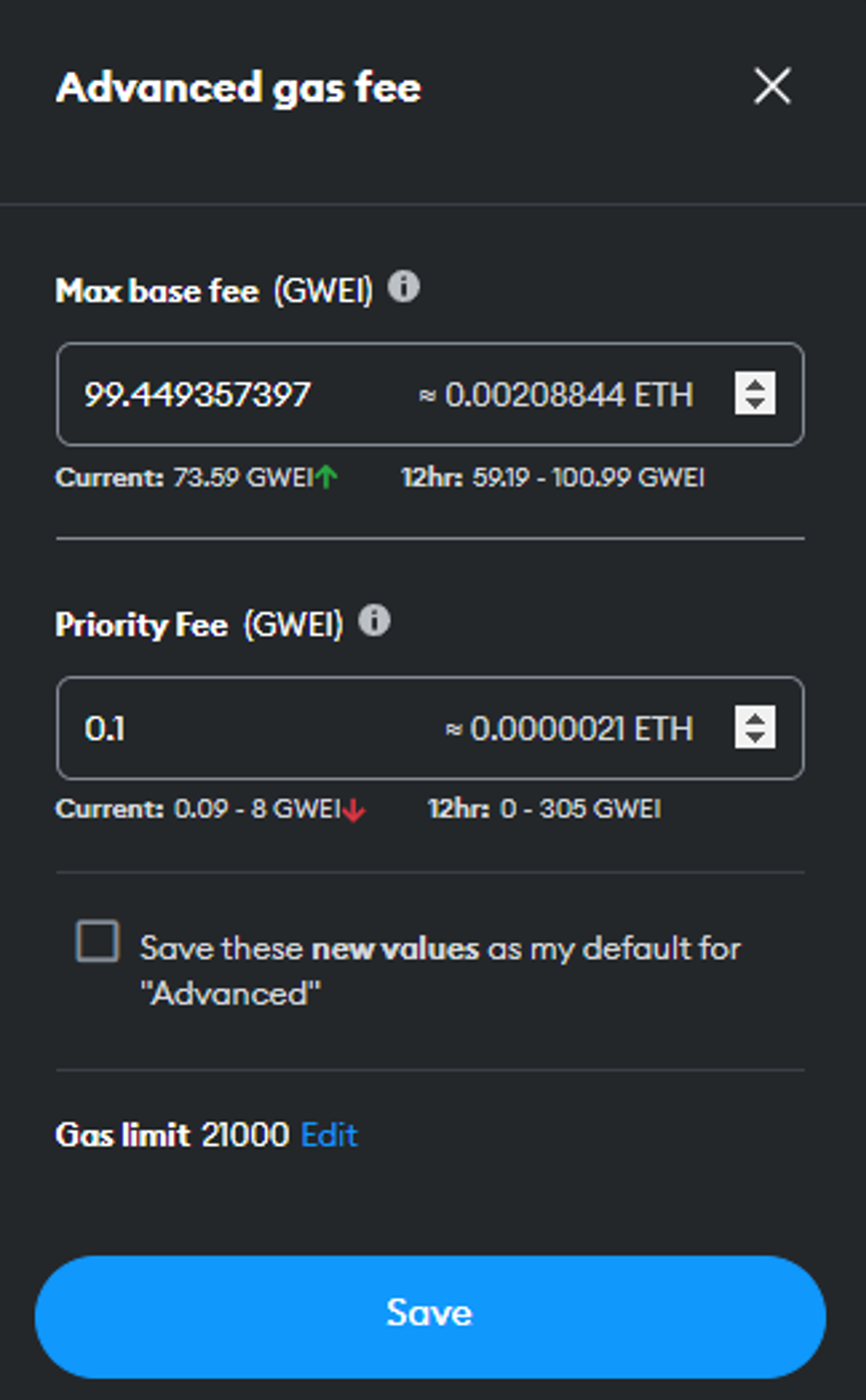
Gas settings from inside Metamask browser extension
To sum it up, gas is the measure of computational work required for a transaction on the Ethereum blockchain, and Gwei is the price you're willing to pay for each unit of gas. The relationship between gas and Gwei determines the cost of a transaction and influences how quickly it gets processed by nodes.
How to determine when gas will be at its lowest?
To answer this, we must first understand what causes the price of gas to rise.

Several factors can contribute to fluctuations in gas prices on the Ethereum network:
1. Network congestion: When there's a high demand for processing transactions, the Ethereum network may become congested. This can happen due to high trading volume, popular ICOs (Initial Coin Offerings), or new dApps generating significant traffic. In such cases, users are likely to set higher gas prices to prioritize their transactions, causing the average gas price to increase.
2. Gas price recommendations: Wallets and other Ethereum services often provide gas price recommendations based on current network conditions. Users who follow these recommendations may cause a general increase or decrease in gas prices, depending on the suggested values.
3. Gas limit: The Ethereum network has a gas limit per block, which is a cap on the total amount of gas that can be included in a single block. When the gas limit is reached, additional transactions have to wait for the next block. If the gas limit is consistently reached due to high network activity, it can contribute to increased gas prices, as users compete for the limited space in each block.
4. Network upgrades and improvements: Changes in the Ethereum protocol, such as network upgrades or scalability improvements, can influence gas prices. For example, the introduction of Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) aimed at reducing transaction costs or optimizing resource usage can affect gas prices.
5. Speculative behavior: As with any market, speculative behavior can influence gas prices. Traders and users may attempt to predict future gas prices based on historical trends or current events and adjust their gas prices accordingly.
It's worth noting that gas prices can be volatile and change rapidly due to these factors. However, ongoing development in the Ethereum ecosystem, such as the transition to Ethereum 2.0 and the implementation of Layer 2 scaling solutions, aims to address these issues and reduce gas prices over time.
Ok so how do I know when gas will be cheapest for me?
Monitoring gas isn’t as scary as one might think. Taking into account everything we discussed in the previous section, we (thirdweb) have as a handy tool you can use for starters, where you can see live gas estimations for things such as contract deployment and mints. And one of the coolest features is it can display the cost in both ETH and USDC values!
- Transaction cost in ETH
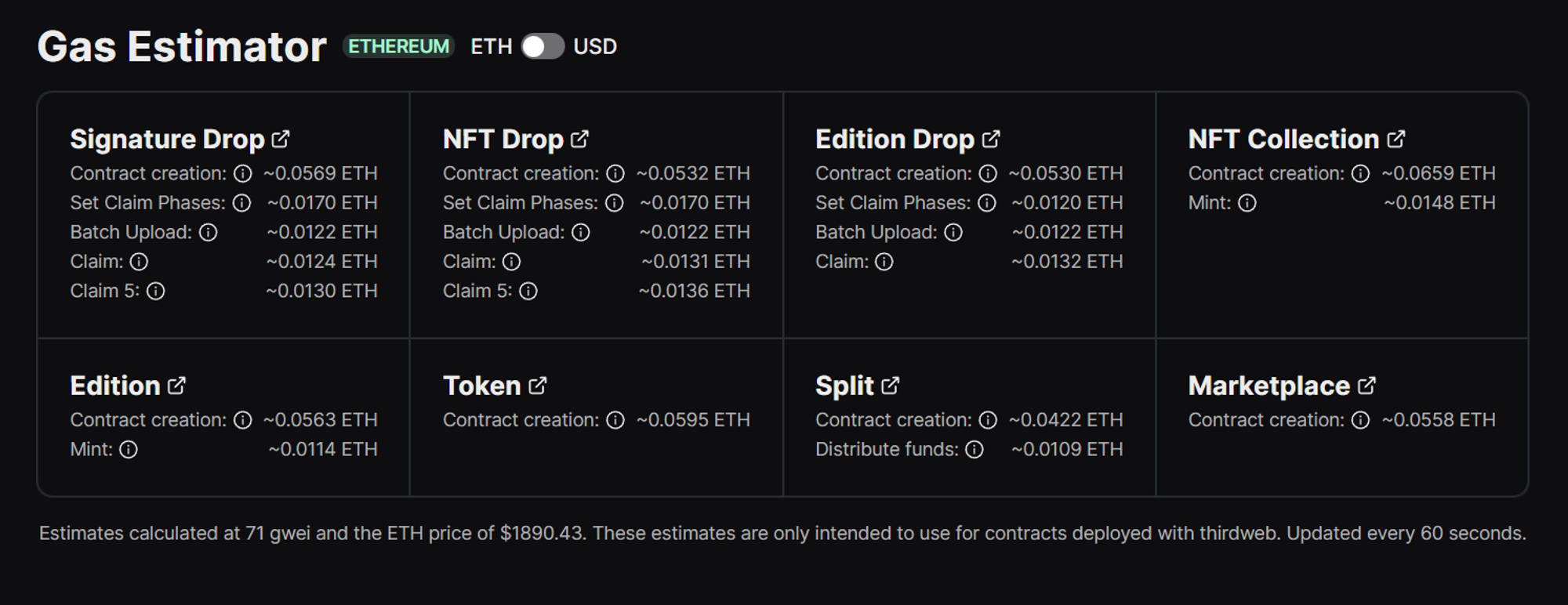
- Transaction cost in USD
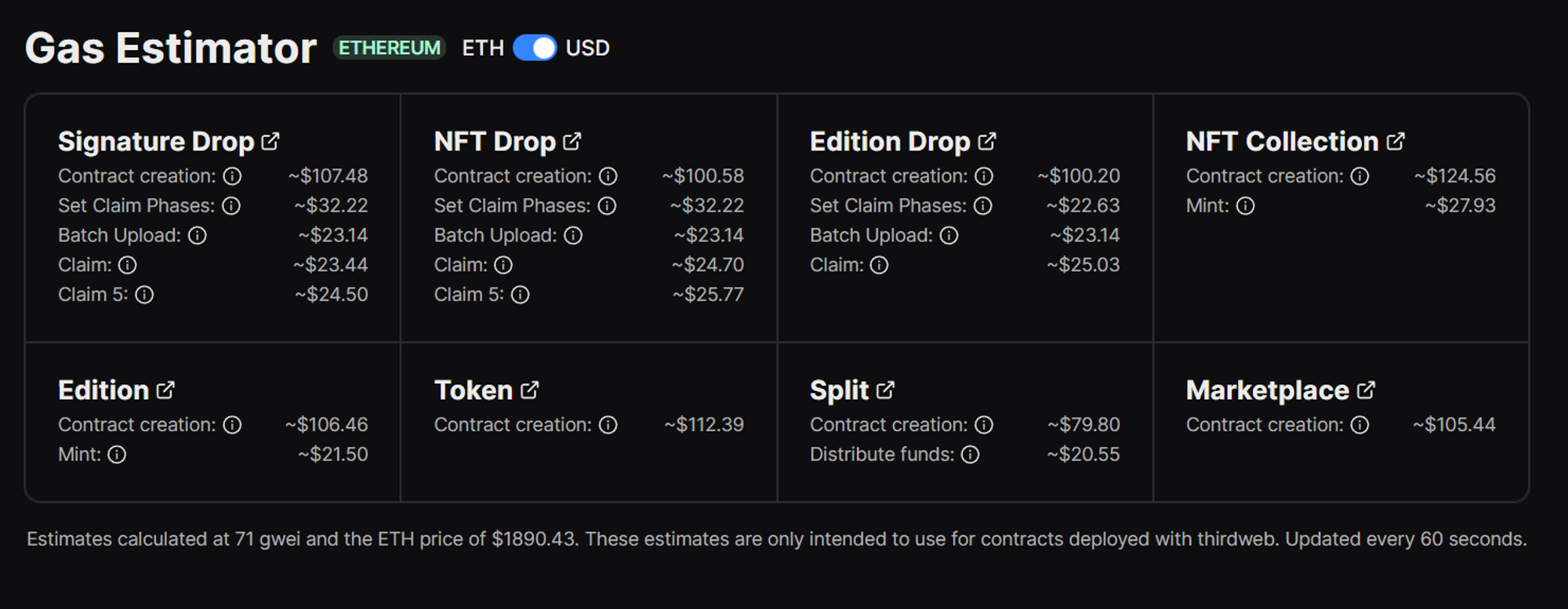
You can share this tool with your community to help them understand when it best to transaction and how much that can expect to pay based on the current Gwei price.
Other gas-saving solutions
1. Off-peak hours: Gas prices tend to be lower during off-peak hours when the network is less congested. Typically, these periods are during nighttime or weekends in regions with high Ethereum usage. As of the time of this forum, low gas hours are currently between 5:00 am CST and 7:00 am CST, this is always subject to change as the window does migrate around all hours of the day.
2. Historical data: Analyzing historical gas price data can help you identify patterns and trends. Websites like EthereumPrice provide historical gas price charts that can help you make informed decisions.
3. Wallet settings: Most Ethereum wallets allow you to manually set the gas price for your transactions. You can choose a lower gas price, but keep in mind that this might result in slower transaction confirmation times, especially during periods of high network congestion.
4. Gas price prediction algorithms: Some advanced users and developers rely on gas price prediction algorithms that analyze historical and real-time data to forecast short-term gas price trends. These algorithms might be helpful in determining when gas prices are likely to be cheaper, but their accuracy may vary.
While there's no foolproof way to predict the cheapest gas prices, employing these strategies and tools can help you optimize your transactions and minimize gas costs. Keep in mind that lower gas prices may lead to slower transaction confirmations, so it's essential to balance cost and speed based on your requirements.
Can’t get this working? If you’ve followed the above and still have issues, contact our support team for help.